从零配置 Linux
Linux Server Configuration
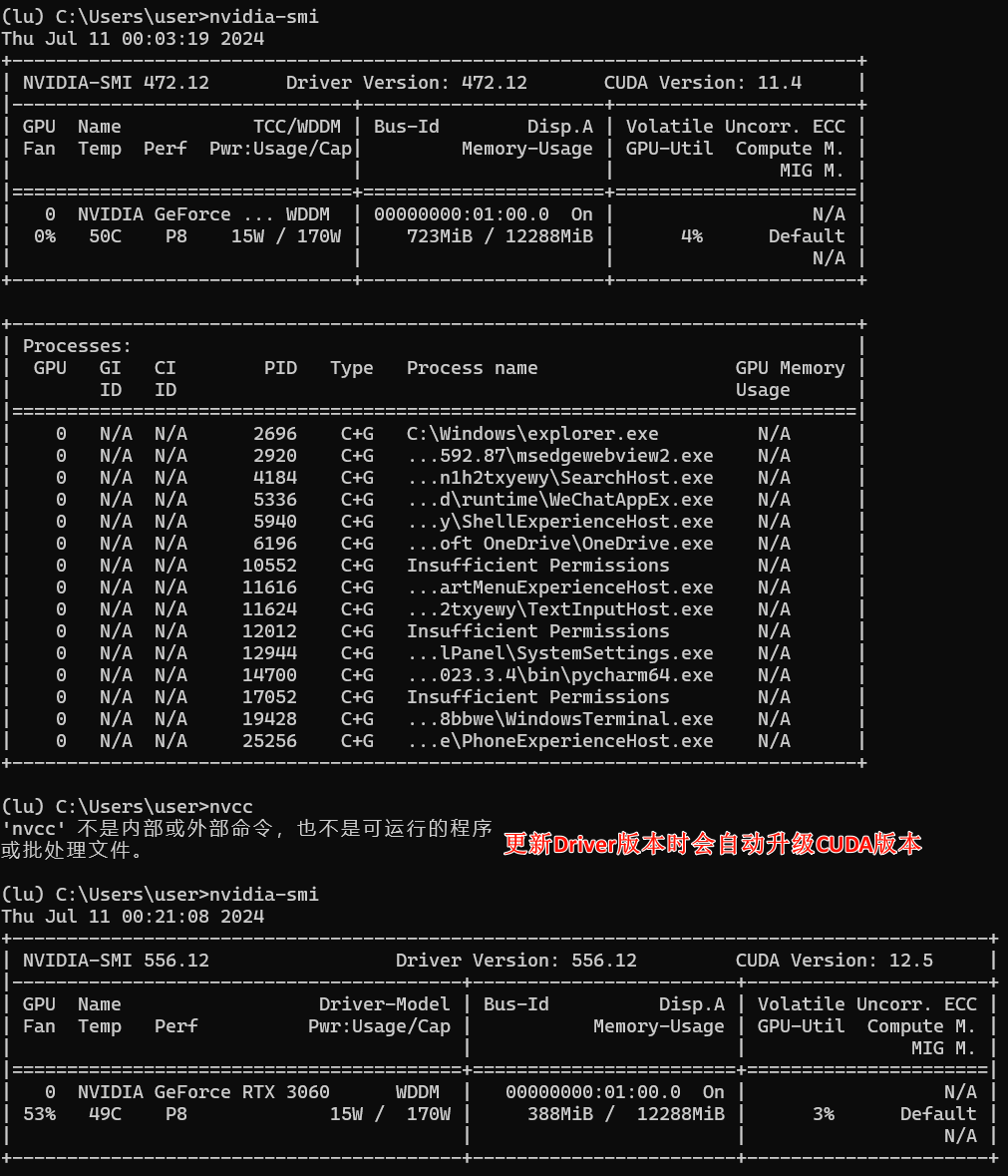
CUDA、CUDA toolkit、cuDNN、NVCC 关系
CUDA Toolkit 和 Driver Version版本对应,版本对应2
下载:Nvidia Driver驱动,CUDA Toolkit Archive,CUDA Toolkit Latest,cuDNN
centos 中以root身份创建新用户并授权
文件夹之间软链接
1.cd <TARGET PATH> 新建空文件夹 .vscode-server
2.cd ~ 删除用vscode远程连接时自动下载的 .vscode-server(没有则下一步)
3.ln -s /<TARGET PATH>/.vscode-server ~/.vscode-server 将 ~/.vscode-server 链接到 /<TARGET PATH>/.vscode-server
4.通过vscode远程连接服务器,自动下载的 .vscode-server 会存到 /<TARGET PATH>/ 下
5.cd ~ && ll -a 检查链接,.vscode-server -> /<TARGET PATH>/.vscode-server 表示成功
6.在vscode的设置中将 远程和工作区 的 search.followSymlinks 设置为 False,原因
文件夹所有者及权限修改
chown -R <USER NAME>:<USER GROUP> <PATH>:-R 递归修改路径下所有文件(夹)的所有者
chmod 755 <PATH> / chmod -R 755 <PATH>:修改文件夹下所有文件(夹)用户的权限;-R 加与不加效果一样,均会递归更改路径下所有文件(夹)的权限
1
2
3
所有者(用户)权限 rwx:读(4) + 写(2) + 执行(1) = 7
同组用户权限 r-x:读(4) + 不写(0) + 执行(1) = 5
其他用户权限 r-x:读(4) + 不写(0) + 执行(1) = 5
测试 ip 地址及端口的连通性,查看防火墙状态、开放端口
以 172.27.33.63:1234 为例,
ping 172.27.33.63,如果不通,说明ip 地址无法访问;如果通了进行下一步telnet 172.27.33.63 1234,如果不通,进行下一步;如果通了说明ip 地址及端口没有问题sudo firewall-cmd --query-port=1234/tcp,如果显示 no,进行下一步添加指定需要开放的端口:
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=1234/tcp --permanent重载入添加的端口:
sudo firewall-cmd --reload查询指定端口是否开启成功:
sudo firewall-cmd --query-port=1234/tcp如有需要,移除指定端口:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-port=1234/tcp
/etc/hosts 配置本地DNS
1./etc/hosts 文件的作用是将主机名(域名)映射到IP地址,提供本地 DNS 功能。在操作系统解析域名时,它首先会查阅该文件,如果找到了对应的IP地址,就会直接使用该地址,而无需再通过外部 DNS 服务器查询。通过 ping 域名的方式获取对应的IP地址
2./etc/host.conf 中 multi on:
负载均衡:在一些场景下,一个域名可能会指向多个服务器IP地址(多A记录),以实现负载均衡。如果 multi on,那么系统会返回多个IP地址,客户端可以选择其中一个进行连接 冗余和容错:当一个主机名绑定了多个IP,某个IP不可用时,返回多个IP地址可以让系统尝试其他的IP地址
服务器配置 clash 代理
下载 clash-linux-amd64-v1.18.0.gz:wget https://github.com/Kuingsmile/clash-core/releases/download/1.18/clash-linux-amd64-v1.18.0.gz
获取 config.yaml:Clash for Windows - Profiles - config.yaml - 右键 Show in folder - 终端运行 scp config.yaml username@ip:/path/
Miniconda - python env
1.在 /data/<USER NAME> 指定目录下安装miniconda
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh
2.添加 Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh 在 /data/<USER NAME>下的权限后,文件名变成绿色(可执行)
chmod a+rwx Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh 后 sh Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh ,修改安装路径为 /data/<USER NAME>/miniconda3
将 /data/<USER NAME>/miniconda3/bin 添加到所有系统路径$PATH之后并重新加载
echo 'export PATH="$PATH:/data/<USER NAME>/miniconda3/bin"' >> ~/.bashrc && source ~/.bashrc
(可选) conda init 写入代码到 ~/.bashrc,设置登录服务器自动激活 base环境
3.创建新环境并指定安装其他版本如3.10 的python conda create -n <ENV NAME> python=3.10
4.创建新环境并指定路径 conda create python=3.10 --prefix /data/<USER NAME>/miniconda3/envs/<ENV NAME> 来代替默认路径 ~/.conda/envs。或修改 conda config --add envs_dirs /data/<USER NAME>/miniconda3/envs 避免每次安装时指定 prefix
5.pip 换用国内镜像源,如阿里源https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple,中科大源https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple,豆瓣源http://pypi.douban.com/simple
1
2
3
pip install <package_name> -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple # 暂时换源
pip config set global.index-url https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple # 永久换源
pip config unset global.index-url # 换回默认源
6.删除环境 conda remove -n <ENV NAME> --all / conda env remove --name <ENV NAME>
conda 相关命令
conda env export --name <ENV NAME> > environment.yml:导出环境包(> 会覆盖文件内容,>> 会在文末追加内容,若文件不存在都会新建文件。)
conda run -n <ENV NAME> python your_script.py:任何环境下指定conda环境运行命令,避免频繁切换环境
conda安装虚拟环境时发生ClobberError:先运行 conda clean --all,再运行安装命令
conda activate 是 Conda 4.4 的新特性,更加现代和标准,而 source activate 是 Conda 4.3以前的旧方式
pip install . vs pip install -e .
使用 pip install -e .(editable 模式)安装项目时,Python 会创建一个指向项目源代码目录的符号链接,而不是将文件复制到 site-packages 目录。这意味着你对源代码的任何更改会立即在安装的包中生效,无需重新安装。这对于开发和调试非常有用,因为你可以实时看到代码修改的效果
Jupyter Lab
pip install jupyterlab 安装后 jupyter lab / jupyter-lab 启动
Jupyter Hub
直接部署:
1
2
3
4
5
conda install -c conda-forge jupyterhub` #不推荐 pip安装
jupyterhub --generate-config #生成jupyterhub_config.py
echo "c.JupyterHub.authenticator_class = 'dummy'" >> jupyterhub_config.py #设置用户名
echo "c.DummyAuthenticator.password = 'yourpassword'" >> jupyterhub_config.py #设置密码
jupyterhub --ip 10.0.1.2 --port 443 #启动
docker 部署:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
docker run -p 8000:<SERVER PORT> -d --name jupyterhub quay.io/jupyterhub/jupyterhub jupyterhub #运行容器
docker exec -it jupyterhub bash #进入容器内bash
jupyterhub --generate-config #生成jupyterhub_config.py
echo "c.JupyterHub.authenticator_class = 'dummy'" >> jupyterhub_config.py #设置用户名
echo "c.DummyAuthenticator.password = 'yourpassword'" >> jupyterhub_config.py #设置密码
exit #退出容器bash
docker stop <CONTAINER ID>
docker start <CONTAINER ID> #修改完配置重启容器
此时 jupyterhub 从容器的 8000 端口映射到服务器的 <SERVER PORT> 端口,通过 ssh -L <LOCAL PORT>:localhost:<SERVER PORT> <USERNAME>@<IP ADDRESS> 将 jupyterhub 从服务器的 <SERVER PORT> 端口映射到本地端口 <LOCAL PORT>。本地访问 http://localhost:<LOCAL PORT>/
tmux
tmux 是一个终端多路复用器,允许你在一个终端窗口中运行多个终端会话,并且可以在这些会话之间自由切换,非常适用于远程会话管理和多任务处理,Windows系统可通过MSYS2使用
tmux ls 查看现有的会话
tmux new -s <SESSION NAME> 新建会话
tmux attach -t <SESSION NAME> 接入会话
Ctrl+b d / tmux detach 分离会话
tmux kill-session -t <SESSION NAME> 杀死会话
screen 后台任务管理
screen -S <SOCKET NAME> 创建新socket
screen -ls 查看所有创建的sockets
screen -d -r <SOCKET NAME> 切换到socket
screen -X -S <SOCKET NAME> quit 关闭socket
Ubuntu
Ubuntu docker.io 和 docker-ce 安装
docker.io 采用 apt 管理依赖,由Debian维护;docker-ce 采用 go 管理依赖,由docker官方维护 安装文档
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 安装 docker.io
sudo apt install docker.io
# 安装 docker-ce
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/docker-ce/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs)\
stable"
sudo apt-get update # 更新包的安装列表,通过 sudo apt-get upgrade 更新包
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc
sudo apt-get install docker-ce
Ubuntu Docker一键部署Jupyter Notebook并实现远程访问本地笔记 视频 文档
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
# Add Docker's official GPG key:
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg
$ sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
$ sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
# Add the repository to Apt sources:
$ echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
$ sudo apt-get update
# 安装docker包
$ sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
# 镜像测试
$ sudo docker run hello-world
# 拉取 `jupyter/base-notebook` 镜像
$ sudo docker pull jupyter/base-notebook
# 查看所有拉取的镜像,区别于`sudo docker ps -a` 查看所有容器
$ sudo docker images
# 创建容器,将被本地/外部端口8888映射到容器/内部端口8888
$ sudo docker run -d -p 8888:8888 jupyter/base-notebook
# 查看正在运行的容器,获取网页8888端口登陆token
$ sudo docker ps
$ sudo docker logs <CONTAINER ID>
# 安装内网穿透工具 cpolar,端口 9200,登陆邮箱 15345180091@163.com
$ curl -L https://www.cpolar.com/static/downloads/install-release-cpolar.sh | sudo bash
$ sudo systemctl enable cpolar
$ sudo systemctl start cpolar
# 查看状态,停止服务
$ sudo systemctl status cpolar
$ sudo systemctl stop cpolar
Ubuntu新系统安装显卡驱动
法一(推荐):
settings-about-software updates-addtional drivers-切换到最新的Using NVIDIA driver metapackage
法二:
更新驱动 sudo ubuntu-drivers autoinstall
法三:
官网下载驱动安装 视频教程
下载官网驱动安装 sudo ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-550.54.14.run -no-x-check
卸载官网驱动 sudo ./NVIDIA-Linux-x86_64-550.54.14.run -uninstall
清理残留文件 sudo apt --purge remove nvidia* sudo apt autoremove
Ubuntu新系统安配置ssh方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 0.查看系统信息
$ uname -a
$ cat /etc/lsb-release
# 1.修改root密码并切换到root
$ sudo passwd root
$ su root
# 2.卸载重装
$ apt-get update
$ apt-get remove openssh-server
$ apt-get install openssh-server
# 3.编辑sshd_config
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Port 22
PermitRootLogin yes
PasswordAuthentication yes
# 4.重启服务,检查状态
$ service ssh --full-restart
$ service ssh status
# 5.ifconfig后查看etho下的inet,形如172.27.26.118
$ sudo apt install net-tools
$ ifconfig
在同一局域网下的其他终端上通过ssh root@172.27.26.118 -p 22(端口号默认22可使用ssh root@172.27.26.118)进行SSH连接。第3步中默认的PermitRootLogin prohibit-password如果不改成PermitRootLogin yes,那么只能以普通用户如ssh yuy4o@172.27.26.118登录,无法以超级管理员root登录。
无公网IP时如何SSH远程连接Ubuntu系统
参照 视频、文档 中安装内网穿透工具 cpolar,端口 9200,登陆注册邮箱xxxxxxxxxxx@163.com,获得ssh对应的公网地址比如tcp://5.tcp.vip.cpolar.cn:10713
在其他终端上,输入ssh <ubuntu用户名>@5.tcp.vip.cpolar.cn -p 10713,输入对应密码即可连接
ubuntu20.04安装Linux原生微信
ubuntu22.04 添加中文输入法
CentOS 8
centos8 解决 Failed to download metadata for repo ‘appstream’
APT
不只Ubuntu,其实Debian系统的系统(Debian,Ubuntu,Deepin,Raspbian等)都可以使用apt命令安装软件。在Ubuntu 16 之前要使用apt-get install 软件包来安装,在Ubuntu 16 之后可以直接使用apt install 软件包来安装。
apt 命令用法:
更新软件列表:apt update -y
搜索软件: apt search 关键字
显示软件包详情:apt show 软件包名
显示安装列表:apt list; 显示可升级的安装列表:apt list –upgradable
安装软件:apt install 软件包名
升级指定软件:apt upgrade 软件包名;升级所有可升级的软件:apt upgrade
卸载软件:apt remove 软件包名
卸载软件并移除软件依赖:apt autoremove 软件包名
卸载软件并删除配置文件:apt remove 软件包名 –purge
在终端占直接运行命令就可以安装,比如使用命令安装 gimp sudo apt install gimp -y
SNAP
snap是在Ubuntu 16 新添加的一种软件包格式。这种格式把软件运行所需的依赖全部打包到软件包里面, 运行的时候持载到一个虚拟的环境里面运行。所有这种格式的软件包安装时不会破坏系统现有的软件包依赖。
snap命令用法:
搜索软件包:snap find 关键字
显示软件包详情:snap info 软件包名
安装软件包:snap install 软件包名
升级指定软件:snap refresh 软件包名
升级所有可以升级的软件:snap refresh
卸载软件:snap remove 软件包名
也是直接在终端运行命令就可以安装,比如使用命令安装wps sudo snap install wps-2019-snap
DPKG
上述方法都只能安装已经添加的软件源里面的软件。但像网易云音乐、百度网盘这些并没有在软件源里面,而是在官网提供deb后缀的软件包下载,这种软件我们就要用到dpkg命令来安装了 sudo dpkg -i 文件名.deb
Linux Commands
ip address / ifconfig 显示和管理网络接口信息
top -u <USER NAME> 动态展示用户进程及资源占用,htop
ps -u <USER NAME> 静态展示用户进程及资源占用
ps -u -p <PID> 根据进程号查进程
ps -o ppid,cmd -p <PID> 根据进程号查看进程的运行命令
ps aux | grep python / ps -ef | grep python 查看所有python相关的进程
df -h 查看硬盘剩余空间
du -h 查看路径下文件占用硬盘空间,du -sh * 查看路径下所有文件夹各自占用的总空间,du -sh .[!.]* * 查看所有文件夹包括隐藏文件夹各自占用的总空间
free -h 查看内存使用空间
sudo lsof -i :<PORT NUMBER> 查看占用端口的所有进程信息;sudo lsof -i tcp:<PORT NUMBER> 查看占用TCP端口的进程信息
find <PATH> -name "<FILE NAME>" 2>/dev/null 在路径下根据文件名查找文件



Comments powered by Disqus.